Dàn bài IELTS Writing Task 1 dạng bài nhận xét biểu đồ tròn
Câu 1. Cách nào dưới đây là cách tốt nhất để dàn bố cục trong bài nhận xét?
A) Viết 1 đoạn văn về immigration và 1 đoạn văn về emigration
B) Viết cùng lúc về cả 2 charts mà trong đó so sánh từng lý do
Câu 2. Thì nào nên được sử dụng để viết bài này?
A) Thì quá khứ (past tense)
B) Thì hiện tại (simple tense)
Câu 3. Có thể đề cập đến những sự tăng (increases) hay giảm (decreases) khi viết nhận xét cho hai biểu đồ này không?
A) Có thể
B) Không thể
Sau đây là một số điểm chính để viết nhận xét cho pie chart:
Thứ tự quan trọng: 'tốt khoe, xấu thì cho lui về sau'
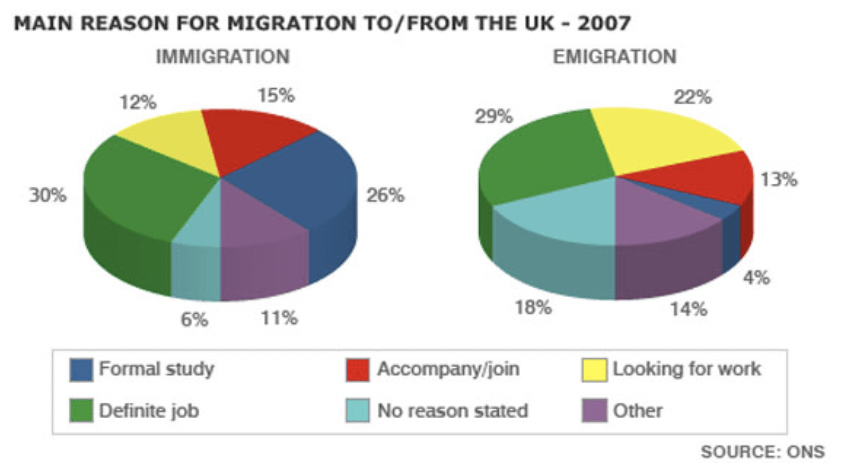
Những yếu tố nào chiếm tỷ trọng cao nhất, 'miếng bánh' to nhất, thì sẽ được đưa lên trước. Trong biểu đồ tròn này thì các yếu tố đó là: definite job, looking for work, và formal study sẽ được ưu tiên đưa ra nói trước theo thứ tự mức độ quan trọng. Những yếu tố như other hay no reason stated không quan trọng thì nên để sau cùng.
Nói cho dễ nhớ là cứ số liệu nào to thiệt to, đẹp thiệt đẹp thì bạn đưa lên trước . Tốt thì phải khoe chứ. Còn số liệu nhỏ nhỏ, ít ít thì viết sau, cho lui về hậu cung.
Phân tích biểu đồ: đi theo chiều ngang
Đối với Pie chart, cách logic nhất để xếp các thông tin với nhau là so sánh các đối tượng theo chiều ngang, tập trung vào những điểm giống nhau và khác nhau. Đừng viết nhận xét từng biểu đồ tròn riêng biệt, tức là đừng nhận xét theo chiều dọc. Bạn cũng sẽ áp dụng cách làm tương tự khi nhận xét Table (bảng số liệu)
Để minh hoạ sự ngang - dọc kia cho dễ hiểu, 2 biểu đồ tròn ở trên nếu được trình bày theo dạng Table thì sẽ thế này.
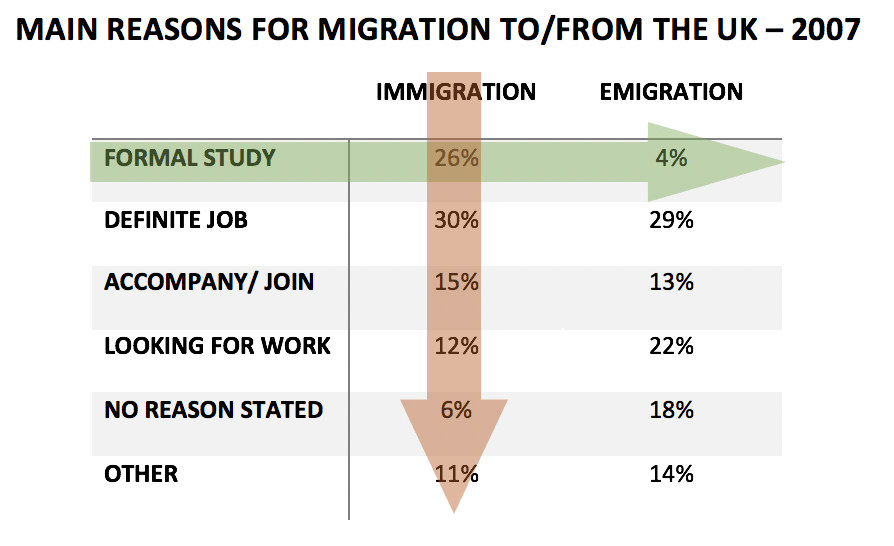
Nhận xét theo chiều ngang, tức là sẽ đi theo mũi tên xanh lá. Bạn sẽ nhận xét về yếu tố formal study, trong đó nói tỷ lệ của lý do này ở immi là 26%, trong khi ở emi chỉ có 4%. Tương tự, bạn nhận xét yếu tố tiếp theo, ví dụ như definite job và cứ thế cho đến hết 6 lý do.
Nhận xét theo chiều dọc tức là bạn nhận xét từng cột riêng lẻ, hoặc nếu là biểu đồ tròn là đang nhận xét từng biểu đồ riêng lẻ và cách này không nên vì nó không thể hiện được sự tương quan giữa 2 cột/ biểu đồ. Cách này không được khuyến khích.
Nhóm các số liệu theo sự giống nhau: 'ngưu tầm ngưu, mã tầm mã'
Quy tắc nhóm số liệu, cũng na ná như cách nhóm số liệu ở biểu đồ đường, hay biểu đồ cột, những số liệu lớn/ nổi bật sẽ gom chung lại viết vào 1 đoạn. Đoạn còn lại viết các số nhỏ hơn hay các yếu tố phụ khác. Hiểu nôm na là 'con nhà giàu' thì vào hội nhà giàu, 'con nhà nghèo' thì vào hội nhà nghèo. Ngưu tầm ngưu, mã tầm mã.
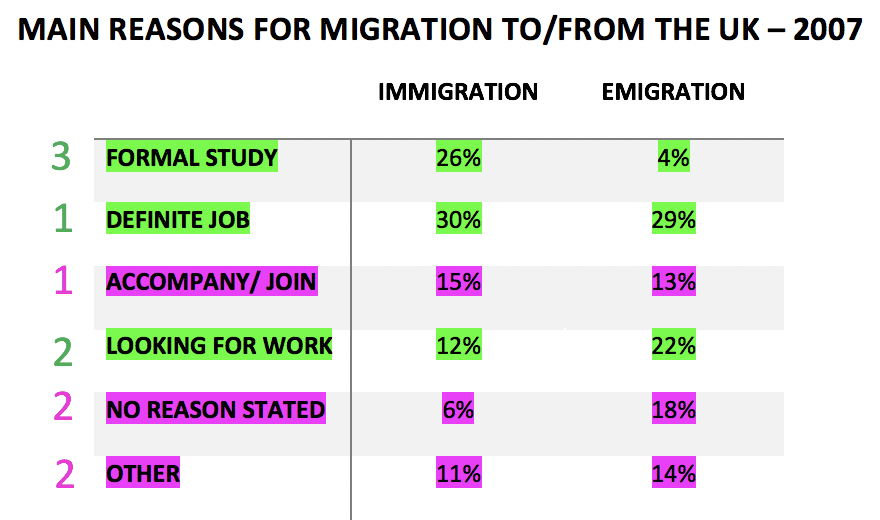
Theo như quy tắc trên:
Đoạn body paragraph 1 sẽ nói về 'hội nhà giàu' sẽ gồm: definite job, looking for work & formal study. Thứ tự xuất hiện trong hội này vẫn áp dụng quy tắc 'tốt khoe, xấu lui'. Definite job số liệu lớn ở cả Immi và Emi --> đưa lên đầu tiên (số 1), looking for work số liệu cũng tương đối lớn cả cả Immi và Emi --> nói thứ 2, formal study cao có mỗi bên Immi nhưng thấp bên Emi nên sẽ nói thứ 3.
Đoạn body paragraph 2 sẽ nói về 'hội nhà nghèo', sẽ gồm: accompany/join, other và no reason stated. Thứ tự xuất hiện: 1) là accompany/ join, 2) no reason và other sẽ được gom lại nói chung vì cả 2 mục này đều không quan trọng bằng lý do kia.
Các cách diễn đạt để nhận xét Pie Chart
Các từ vựng quan trọng khi nhận xét Pie Chart là proportions và percentages, cách diễn đạt phổ biến nhất là "the proportion of…" hoặc "the percentage of…"
Thay vì dẫn số % ra, bạn có thể diễn đạt bằng phân số tương ứng của nó:
- 80% = four-fifths | 75% = three-quarters | 70% = seven in ten | 65% = two-thirds | 60% = three-fifths | 55% = more than half | 50% = half
- 45% = more than two-fifths | 40% = two-fifths | 30% = less than a third | 25% = a quarter | 20% = a fifth | 15% = less than a fifth | 10% = one in ten | 5% = one in twenty
Dùng các adverb mang tính ước chừng để nói những con số khoảng, không chính xác:
- 77% = just over/ approximately three-quarters
- 49% = just under/ nearly a half
- 32% = almost a third
Những cách diễn đạt khác:
- Percentage = proportion / number / amount / majority / minority
- 75% - 85% = a very large majority
- 65% - 75% = a significant proportion
- 10% - 15% = a minority
- 5% = a very small minority
Các liên kết từ, từ nối dùng trong so sánh
Liên kết 2 câu mang ý tương phản nhau
- In contrast: The most popular form of holiday among the Welsh was self-catering with over 60% choosing to cook for themselves. In contrast, only 5 % of the English chose this form of vacation and hotel accommodation was much more popular at 48%.
- In comparison: Almost 50% of the English, Scots and Northern Irish chose to stay in a hotel for their holiday. In comparison, staying in self-catering accommodation was much less popular with around 10% of people choosing this.
- However: The general pattern was for hotel accommodation to be the most popular with around half the people choosing it. The majority of the Welsh, however, chose to stay in self-catering accommodation.
- On the other hand: It is clear that a majority of the British chose to stay in a hotel for their holiday. On the other hand, there was an exception to this because over 50% of the Welsh opted for self-catering accommodation.
Liên kết 2 mệnh đề trong cùng 1 câu mang ý tương phản nhau
- while: While there are 4 million miles of train lines in the UK, there are only 3 million in France.
- whereas: Whereas the majority of the French prefer to travel to work by train, only a small minority of the British do.
- although: Although 15% of the French read novels, only 5% of the British do.
- but: 25% of French females study math with a private tutor, but nearly 60% study English with one.
So sánh nhiều nhất/ ít nhất
- The most: The most popular form of entertainment in the UK was going to the cinema.
- The least: The least common form of transport was taking a taxi.
So sánh bằng
- Similar (to)
- The percentages of females and males who studied languages at a university were very similar.
- A similar amount of gas and electricity was used domestically in homes.
- The figures for 2012 were very similar to the figures for 2013.
- Same as …as
- The percentage of females who studied at university in 2011 was almost exactly the same as in 2012
Dùng differ/different/difference
- The amount of time spent at home differed by almost 25% according to gender.
- There was a difference of over 25% in the number of time males and females spent at home.
- This figure was very different among males, only half of whom watched television.
So sánh có số liệu
- [5 million] more/less/fewer: 5 million fewer units of gas were sold in 2014.
- Twice: Twice as many people elected to use gas and not electricity for cooking [note the twice as …as structure] | Twice the amount of gas was used for cooking in this period. [amount đi với danh từ không đếm được]
- Three/four etc times: Four times as many people chose to heat their house with electricity as with gas.
- Half: Half the number of people chose to use gas as electricity. | Electricity was half as popular as gas for cooking.
Vận dụng vào viết bài
Bước 1: Quan sát & chọn lọc các key features (đã làm ở trên)
Bước 2: Lên dàn ý và sắp xếp các key features
| Introduction | Paraphrase lại đề bài |
| Overview | Nói về các đại diện tiêu biểu của 'hội nhà giàu' và 'hội nhà nghèo': có tổng cộng 4 lý do chính cho migration, trong đó nổi bật nhất là definite job, và ít nhất là accompany (đừng đề cập đến other hay nọ reason, bất kể bài này hay bài khác vì các yếu tố này không quan trọng) |
| Body paragraph 1 | Mô tả hội nhà giàu theo thứ tự xuất hiện đã nêu ở trên, dẫn số liệu. |
| Body paragraph 2 | Mô tả hội nhà nghèo theo thứ tự xuất hiện đã nêu ở trên, dẫn số liệu. |
Bước 3: Viết bài
| Introduction | Paraphrase lại đề bài | The pie charts = the given charts show = illustrate the main reasons for migration to and from the UK in 2007 = the primary purposes that people came to and left the UK in 2007 --> The given charts illustrate the primary purposes that people came to and left the UK in 2007. |
| Overview | Nói về các đại diện tiêu biểu của 'hội nhà giàu' và 'hội nhà nghèo': có tổng cộng 4 lý do chính cho migration, trong đó nổi bật nhất là definite job, và ít nhất là accompany (đừng đề cập đến other hay nọ reason, bất kể bài này hay bài khác vì các yếu tố này không quan trọng) | Overall, there were four major factors causing the migration to and from the UK, in which the most influential motivation was a definite career and to accompany a family member was the least common reason. |
| Body paragraph 1 | Mô tả hội nhà giàu theo thứ tự xuất hiện đã nêu ở trên, dẫn số liệu. | In terms of primary purposes, having a fixed occupation in the UK accounted for around 30% of both immigration and emigration to this country. A large number of people, 22%, also emigrated because of job searching, although the proportion of people entering the UK for this purpose was noticeably lower at less than a fifth. Another major factor contributing to a move to the UK was the formal study with over a quarter of people immigrating for their learning, whereas only a small minority, 4%, left the country to serve this purpose. |
| Body paragraph 2 | Mô tả hội nhà nghèo theo thứ tự xuất hiện đã nêu ở trên, dẫn số liệu. | Turning to other minor reasons, proportions of those moving to join a family member were quite similar for immigration and emigration, at 15% and 13% respectively. Although a significant number of people (32%) gave ‘other’ reasons or did not provide a purpose why they emigrated, this accounted for only 17% with regards to immigration. |
Toàn bộ bài viết như sau:
The given charts illustrate the primary purposes that people came to and left the UK in 2007.
Overall, there were four major factors causing the migration to and from the UK, in which the most influential motivation was a definite career and to accompany a family member was the less common reason.
In terms of the principal purposes, having a fixed occupation in the UK accounted for around 30% of both immigration and emigration to this country. A large number of people, 22%, also emigrated because of job searching, although the proportion of people entering the UK for this purpose was noticeably lower at less than a fifth. Another major factor contributing to a move to the UK was the formal study with over a quarter of people immigrating for their learning, whereas only a small minority, 4%, left the country to serve this purpose.
Turning to other minor reasons, proportions of those moving to join a family member were quite similar for immigration and emigration, at 15% and 13% respectively. Although a significant number of people (32%) gave ‘other’ reasons or did not provide a purpose why they emigrated, this accounted for only 17% with regards to immigration.
Phân tích các diễn đạt trong bài
Bài viết bao gồm tất cả các key feature;
Bài viết có sử dụng các transitional words (từ nối) hoặc các conjunctions (liên kết từ) để thể hiện sự liên quan và kết nối giữa các ý (bạn xem các từ được in đậm trong bài)
Bài viết có nhiều sự diễn đạt đa dạng, ít lặp từ:
- reasons = purposes = factors = motivation;
- main = major = primary = principal;
- less common = minor;
- migration = came to and left;
- immigrate/ immigration = entering the UK, a move to the UK;
- emigrate/ emigration = left the country;
Bài viết có các cấu trúc câu với ngữ pháp đa dạng, vận dụng linh hoạt, dùng thì phù hợp;
Thực hành viết bài và nhận phản hồi từ giáo viên Be Ready IELTS trong 48h
Bạn hãy vận dụng các kiến thức trên để viết nhận xét cho các biểu đồ tương tự nhé. Cố gắng là làm bài rồi mới xem bài mẫu nhé.
>>> Xem các đề thể hiện cơ cấu/ so sánh: Pie chart
Nguồn: bài viết này có tham khảo thông tin tại trang https://www.ieltsbuddy.com/ielts-pie-chart.html